United Nations Diabetes Day-Yiduzhengkang takes you to comprehensively understand the application status and R & D trend of hypoglycemic agents

Foreword
Today is United Nations Diabetes Day, formerly World Diabetes Day (WDD). At the end of 2006, the United Nations adopted a resolution to officially rename "World Diabetes Day" as "United Nations Diabetes Day" from 2007, raise experts and academic behaviors to government behaviors of various countries, promote governments and all sectors of society to strengthen the control of diabetes and reduce the harm of diabetes.
According to the World Health Organization, one person dies of diabetes every 10 seconds and one person is amputated due to diabetes every 30 seconds worldwide, and China has 130 million diabetic patients today, ranking first in the world. Diabetes drugs are already the second most common drug after oncology drugs, so let's understand the classification of diabetes drugs before.

Hypoglycemic Agents
一、Hypoglycemic agents are mainly divided into oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin, and oral hypoglycemic agents are divided into the following categories:
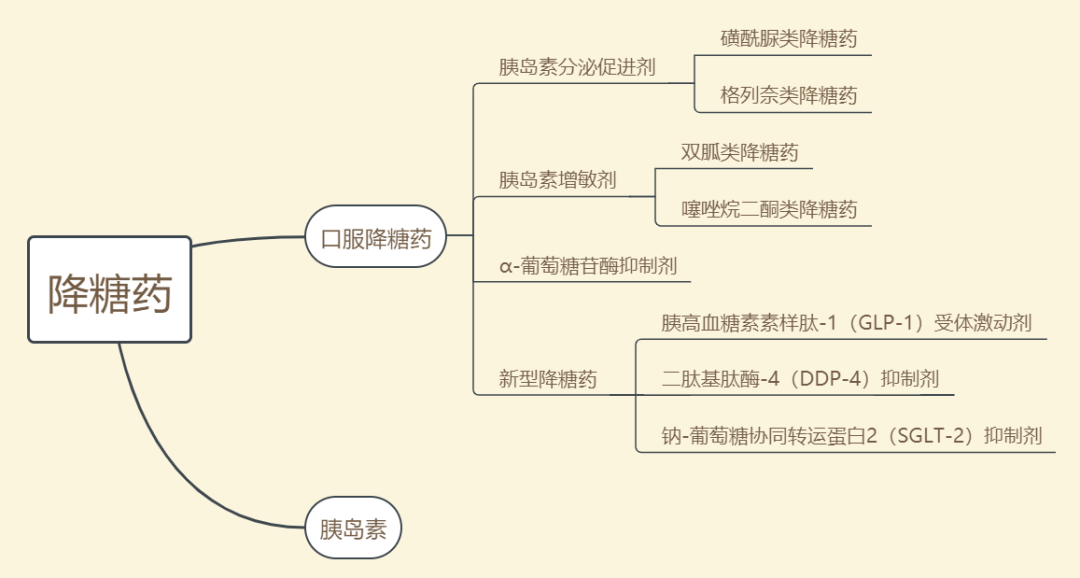
1. Insulin secretagogues
(1) Sulfonylurea hypoglycemic agents: stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. The first generation drugs are tolbutamide and chlorpropamide, the second generation drugs are benzylurea, azide, pyrazine, quinone, and the third generation drugs are methylurea.
(2) Gleevec hypoglycemic agents: stimulate early insulin secretion, rapid absorption, rapid onset, and short duration of action. The representative drugs are repaglinide and nateglinide.
2. Insulin sensitizers
(1) Biguanide hypoglycemic agents: reduce glucose production by the liver and inhibit gluconeogenesis; promote glucose uptake by muscles and increase islet sensitivity. Representative drug metformin.
(2) Thiazolidinediones: After acting on nuclear receptor-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in muscle and adipose tissue, it increases the transcription of numerous related genes affecting glucose metabolism and the synthesis of proteins, ultimately increasing the effect of insulin. The representative drugs are triamcinolone, pyrazone and rosiglitazone.
3. α-glucosidase inhibitors: competitively inhibit various α-glucosidase located in the small intestine, so that the rate of starch decomposition into glucose slows down, thereby slowing down the absorption of glucose in the intestine and reducing hyperglycemia. The representative drugs are acarbose, voglibose, and miglitol.
4. New hypoglycemic agents
(1) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists: GLP-1 receptors are distributed in islet cells, gastrointestinal tract, lung, brain, kidney, hypothalamus, cardiovascular system, liver, adipocytes, skeletal muscle, etc. GLP-1 receptor agonists play a hypoglycemic role by activating GLP-1 receptors. Amylin Pharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly and Company's Byetta Baijieda (exenatide) were marketed in the United States in 2005 and the first GLP-1 receptor agonist to be approved for marketing.
(2) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors: improve α and β cell dysfunction by increasing endogenous active glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide levels. Cetalastine phosphate produced by Merck was approved for marketing in the United States in 2006, is also the first DPP-4 inhibitor in the world, and was marketed in China in 2010. In addition, the representative drugs are vildagliptin from Novartis, salbutamol from Bristol-Myers Squibb, and alogliptin from Wutian, Japan.
(3) Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors: The mechanism of action of SGLT-2 is to specifically inhibit renal glucose reabsorption independent of the degree of β-cell dysfunction or insulin resistance. The representative drug is dapagliflozin developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb and AstraZeneca.
In addition to oral hypoglycemic agents, insulin preparations are animal insulin, human insulin, and insulin analogues. Insulin is a protein hormone secreted by pancreatic β-cells in the pancreas stimulated by endogenous or exogenous substances such as glucose, lactose, ribose, arginine, and glucagon. It is divided into short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulins according to the duration of action. At present, there are first-generation, second-generation and third-generation insulins on the market, and the fourth generation is still under research and development.
Among the drugs used for diabetes, insulin products accounted for 56%, GLP-1 receptor agonists accounted for about 10%, DPP-4 inhibitors accounted for 24%, SGLT-2 inhibitors accounted for 5%, and other traditional small molecule hypoglycemic agents accounted for 4% (acarbose 1%, metformin 1%, urea 1%, others 1%). In China, insulin drugs account for 42.6%, and there is a large space for medication upgrading, of which domestic insulin preparations account for 42.6%, acarbose 20%, metformin 8.8%, repaglinide 7%, and carbamide 6.3%.

二、Analysis of leading enterprises
Domestic European and American enterprises dominate, and Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Lilly, Merck, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Bayer and other giants account for more than 80% of the market share. Novo Nordisk, known as Novo Nordisk, is a world leader in the development and production of insulin for the treatment of diabetes. There are four major categories of diabetes drugs: long-acting insulin, premixed insulin, rapid-acting insulin and GLP-1. The star products are human insulin series - Novo Nordisk, Novo Nordisk, Novo Nordisk, as well as insulin injection products Novo Nordisk 4 (adjustable injection volume), child-specific insulin pen (0.5 unit can be injected), and the latest Novo Pen 5 (with liquid crystal screen digital display); the new generation of rapid-acting insulin injection - Novo Nordisk; insulin secretagogue - Novo Nordisk; human glucagon - Novo Nordisk. In 2019, Novo Nordisk's overall revenue was about 14.567 billion US dollars, accounting for 28.6% of the global overall diabetes drug market; revenue in China was about 12.897 billion yuan, accounting for 27.4% of the Chinese diabetes market. If the diabetes business is split into two major segments: insulin and GLP-1, Novo Nordisk's insulin business revenue in China in 2019 was about 10.273 billion yuan, accounting for 49.8% of the Chinese insulin market; GLP-1 business revenue was about 926 million yuan, accounting for 92.8% of the Chinese GLP-1 market.
三、 Analysis of R & D trends
At present, the global trend of diabetes research and development has the characteristics of drug combination, dosage form innovation, improving SGLT2 drug tolerance and insulin development, of which the trend of new hypoglycemic agents research and development can be described as aggressive. The advantage of GLP-1 receptor agonists is that they lower blood glucose with additional cardiovascular benefits, can reduce food intake and delay gastric emptying, are beneficial for weight control, and have a significantly lower incidence of hypoglycemic events than insulin. SGLT-2 is a newly discovered new target for the treatment of diabetes. In addition to the above introduced effects, it does not depend on the degree of abnormal function of β cells or insulin resistance, the effect will not decrease with the failure of β cell function or severe insulin resistance, there will be no adverse reactions caused by traditional drugs, and it is a new way for the treatment of diabetes. In addition, DDP-4 inhibitors, as new hypoglycemic agents, can increase insulin levels, reduce blood glucose, and are less likely to induce hypoglycemia and increase body weight.
四、R & D Data Analysis
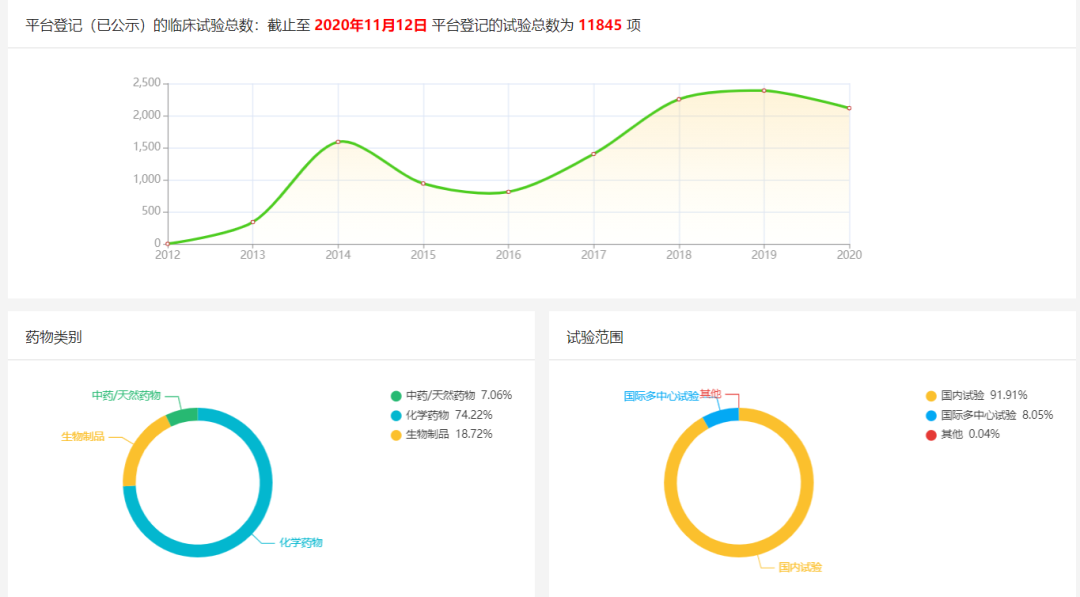
According to IDF (International Diabetes Federation) data, China is the largest country with diabetes in the world, but the awareness rate of Chinese patients with diabetes is only 30%, of which about 25% of patients are treated, so there is still a huge demand in the diabetes market in China. According to CDE data, as of November 12, 2020, there have been 11,845 trials related to diabetes registered on the platform, of which traditional Chinese medicines/natural medicines account for 7.06%, chemical drugs account for 74.22%, and biological products account for 18.72%; domestic trials account for 91.91%, international multicenter trials account for 8.05%, and other trials account for 0.04%.
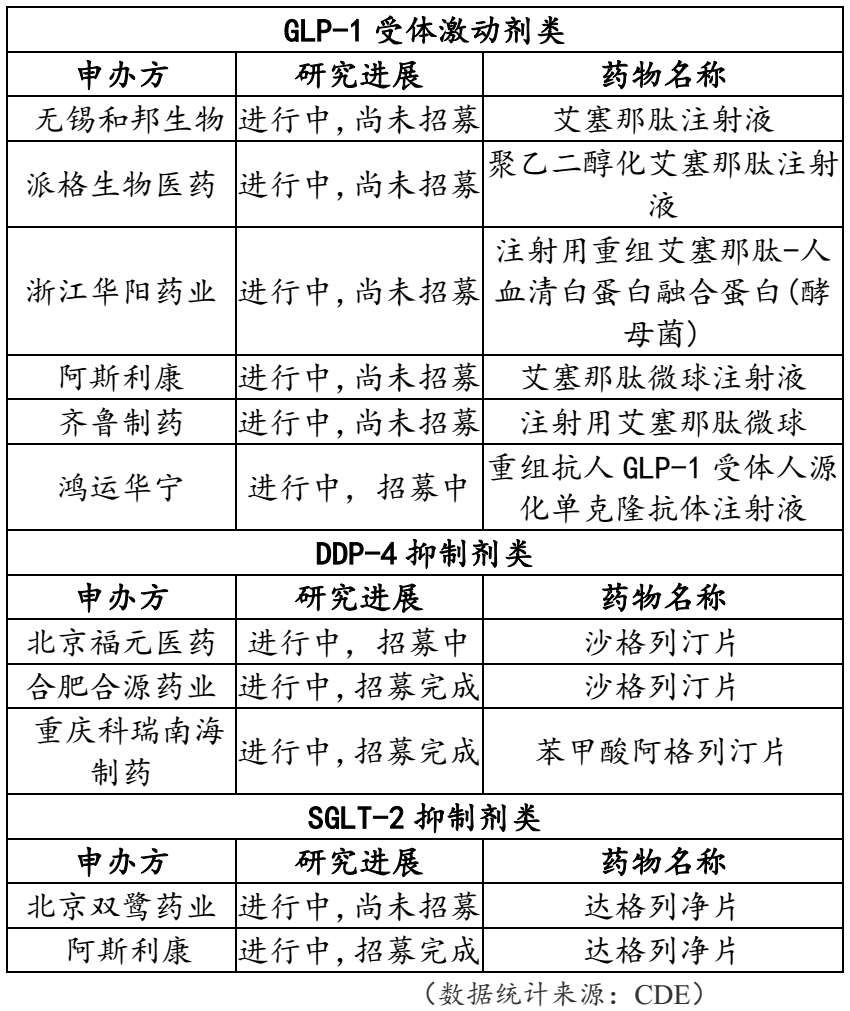
Ongoing new antidiabetic drug research program registered by CDE:
Summary: Yeedozencom is committed to helping the development of drugs in the field of diabetes
At present, China is still dominated by generic drugs from local enterprises, and foreign enterprises dominate innovative drugs. As a professional CRO company, Yiduzhengkang has deep cooperation with domestic and foreign pharmaceutical companies in the field of diabetes, and the study drugs involve oral (α-glucosidase inhibitors, biguanides) and insulin. In April 2020, Yidu Zhengkang successfully assisted Shenzhen Zhonglian Pharmaceutical's "Metformin Hydrochloride Tablets 0.5g" to pass the consistency evaluation. Yi Du Zhengkang believes that with the continuous strengthening of patient education measures by the Chinese government, as well as many media paying attention to the current situation of diabetes in China, more and more knowledge popularization and news reporting, the public's awareness of diagnosis and treatment will be gradually improved, and the continuous progress of R & D technology of local enterprises will be conducive to the development of the diabetes market in China.
REFERENCES:
[1] There is no double in the medical world. Deep Analysis of Diabetes Category. Snow Ball Net, March 12, 2017
[2] Sangkushi. Analysis of current situation of oral hypoglycemic agents in China. Health World, 2020-05-16
[3] Fan Wei. Final Edition of New Advances in Diabetes Drug Research and Development. Baidu Library, July 12, 2019
[4] Today's American shares. Novo Nordisk (NVO.US) 2019: China's revenue is 13.2 billion yuan! Somalutin sold $1.685 billion. 2020-02-06
[5] Yang Lijun. International Best Selling Ranking and Development Trend of Antidiabetic Drugs. Health community. July 31, 2014


